The Republic of Ecuador
Ecuador, located astride the equator on Pacific Coast in South America, has an area of 283,560
sq. km. and a population of 17.64 million (2020). Capital: Quito. Agriculture is the mainstay of the economy but there are appreciable deposits of minerals and petroleum. It is the world’s largest exporter of bananas and balsa wood. Coffee, cacao and shrimp are also valuable exports.
What is now Ecuador formed part of the northern Inca Empire until the Spanish conquest in 1533. Quito became a seat of Spanish colonial government in 1563 and part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada in 1717. The territories of the Viceroyalty – New Granada (Colombia), Venezuela, and Quito – gained their independence between 1819 and 1822 and formed a federation known as Gran Colombia.
When Quito withdrew in 1830, the traditional name was changed in favor of the “Republic of the Equator.” Between 1904 civilian governance in 2004, the period has been marred by political instability. Protests in Quito have contributed to the mid-term ouster of Ecuador’s last three democratically elected Presidents. In 2007, a Constituent Assembly was elected to draft a new constitution; Ecuador’s twentieth since gaining independence.
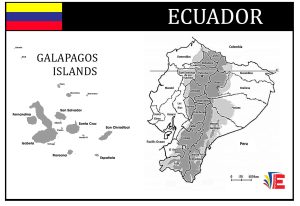
Ecuador Provinces
Ecuador has twenty-four provinces, spanning from its four territory types; Costal, Amazon, Andes (Mountain) , Galapagos (Islands).
Provinces are listed with its own capital.
- Azuay (Cuenca)
- Bolívar (Guaranda)
- Cañar (Azogues)
- Carchi (Tulcán)
- Chimborazo ( Riobamba)
- Cotopaxi (Latacunga)
- El Oro (Machala)
- Esmeraldas (Ciudad Esmeraldas)
- Galápagos (Puerto Baquerizo Moreno)
- Guayas (Guayaquil)
- Imbabura (Ibarra)
- Loja (Loja)
- Los Rios (Babahoyo)
- Manabí (Portoviejo)
- Morona Santiago (Macas)
- Napo (Tena)
- Orellana ( Francisco de Orellana)
- Pastaza (Puyo)
- Pichincha (Quito)
- Santa Elena (Santa Elena)
- Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas (Santo Domingo)
- Sucumbíos (Nueva Loja)
- Tungurahua (Ambato)
- Zamora Chinchipe (Zamora)
Cantons
The Republic of Ecuador is politically divided into provinces, cantons and parishes. There are a total of 24 provinces, which in turn are made up of a total of 221 cantons, and the latter are divided into parishes.
| Region Sierra | Region Sierra | |||
| Azuay | Camilo Ponce Enríquez | Cotopaxi | Latacunga | |
| Chordeleg | La Maná | |||
| Cuenca | Pangua | |||
| El Pan | Pujilí | |||
| Girón | Salcedo | |||
| Guachapala | Saquisilí | |||
| Gualaceo | Sigchos | |||
| Nabón | Imbabura | Antonio Ante | ||
| Oña | Cotacachi | |||
| Paute | Ibarra | |||
| Pucará | Otavalo | |||
| San Fernando | Pimampiro | |||
| Santa Isabel | San Miguel de Urcuquí | |||
| Sevilla de Oro | Loja | Calvas | ||
| Sígsig | Catamayo | |||
| Bolívar | Caluma | Celica | ||
| Chillanes | Chaguarpamba | |||
| Chimbo | Espíndola | |||
| Echeandía | Gonzanamá | |||
| Guaranda | Loja | |||
| Las Naves | Macará | |||
| San Miguel | Olmedo | |||
| Cañar | Azogues | Paltas | ||
| Biblián | Pindal | |||
| Cañar | Puyango | |||
| Déleg | Quilanga | |||
| El Tambo | Saraguro | |||
| La Troncal | Sozoranga | |||
| Suscal | Zapotillo | |||
| Carchi | Bolívar | Pichincha | Cayambe | |
| Espejo | Mejía | |||
| Huaca | Pedro Moncayo | |||
| Mira | Pedro Vicente Maldonado | |||
| Montúfar | Puerto Quito | |||
| Tulcán | Quito | |||
| Chimborazo | Alausí | Rumiñahui | ||
| Chambo | Tungurahua | Ambato | ||
| Chunchi | Baños | |||
| Colta | Cevallos | |||
| Cumandá | Mocha | |||
| Guamote | Patate | |||
| Guano | Quero | |||
| Pallatanga | San Miguel de los Bancos | |||
| Penipe | San Pedro de Pelileo | |||
| Riobamba | Santiago de Píllaro | |||
| Tisaleo | ||||
| Region Costa | Region Costa | |||
| El Oro | Arenillas | Los Ríos | Mocache | |
| Atahualpa | Montalvo | |||
| Balsas | Palenque | |||
| Chilla | Puebloviejo | |||
| El Guabo | Quevedo | |||
| Huaquillas | Quinsaloma | |||
| Las Lajas | Urdaneta | |||
| Machala | Valencia | |||
| Marcabelí | Ventanas | |||
| Pasaje | Vinces | |||
| Piñas | Manabí | 24 de Mayo | ||
| Portovelo | Bolívar | |||
| Santa Rosa | Chone | |||
| Zaruma | El Carmen | |||
| Esmeraldas | Atacames | Flavio Alfaro | ||
| Eloy Alfaro | Region Costa | Jama | ||
| Esmeraldas | Jaramijó | |||
| Muisne | Jipijapa | |||
| Quinindé | Junín | |||
| Rioverde | Manta | |||
| San Lorenzo | Montecristi | |||
| Guayas | Alfredo Baquerizo | Olmedo | ||
| Balao | Paján | |||
| Balzar | Pedernales | |||
| Colimes | Pichincha | |||
| Daule | Portoviejo | |||
| Durán | Puerto López | |||
| El Empalme | Rocafuerte | |||
| El Triunfo | San Vicente | |||
| General Antonio Elizalde | Santa Ana | |||
| Guayaquil | Sucre | |||
| Isidro Ayora | Tosagua | |||
| Lomas de Sargentillo | Santa Elena | La Libertad | ||
| Marcelino Maridueña | Salinas | |||
| Milagro | Santa Elena | |||
| Naranjal | Santo Domingo | La Concordia | ||
| Naranjito | Santo Domingo | |||
| Nobol | ||||
| Palestina | ||||
| Pedro Carbo | ||||
| Playas | ||||
| Salitre | ||||
| Samborondón | ||||
| Santa Lucía | ||||
| Simón Bolívar | ||||
| Yaguachi | ||||
| Los Ríos | Babahoyo | |||
| Baba | ||||
| Buena Fe | ||||
| Region Amazónica | Region Insular | |||
| Morona Santiago | Gualaquiza | Galápagos | Isabela | |
| Huamboya | San Cristóbal | |||
| Limón Indanza | Santa Cruz | |||
| Logroño | ||||
| Morona | ||||
| Pablo Sexto | ||||
| Palora | ||||
| San Juan Bosco | ||||
| Santiago de Méndez | ||||
| Sucúa | ||||
| Taisha | ||||
| Tiwintza | ||||
| Napo | Archidona | |||
| Carlos Julio Arosemena Tola | ||||
| El Chaco | ||||
| Quijos | ||||
| Tena | ||||
| Orellana | Aguarico | |||
| Francisco de Orellana | ||||
| La Joya de los Sachas | ||||
| Loreto | ||||
| Pastaza | Arajuno | |||
| Mera | ||||
| Pastaza | ||||
| Santa Clara | ||||
| Sucumbíos | Cascales | |||
| Cuyabeno | ||||
| Gonzalo Pizarro | ||||
| Lago Agrio | ||||
| Putumayo | ||||
| Shushufindi | ||||
| Sucumbíos | ||||
| Zamora | Centinela del Cóndor | |||
| Chinchipe | ||||
| El Pangui | ||||
| Nangaritza | ||||
| Palanda | ||||
| Paquisha | ||||
| Yacuambi | ||||
| Yantzaza | ||||
| Zamora | ||||